3.9.4. Drawing plants on highly detailed maps
These items are drawn to show three-dimensional vegetation on the map.
Warning
- This is part of an experiment, which is why such items are drawn only on a limited area of highly detailed maps (but you can draw them on any area where the editor allows edits).
- You can edit or redraw simple vegetation items as items with detailed vegetation attributes, but not the other way round (data degradation).
In this section:
3.9.4.1. Drawing and adding attributes to Plant point objects
Don't draw individual plants as point objects (free-standing trees and shrubs) within polygons for urban or forest vegetation (see 3.9.2.1).
After drawing freestanding point objects, set the lawn
type for the existing vegetation polygon.
Note
To change the vegetation type within the polygon, draw all places that you can see in the sources. Don't draw only a part of point plants within one polygon.
However, if the polygon is missing on the map, you may draw only a part of point plants.
Cases when a tree point object overlaps with a polygon whose attributes specify it's occupied by a shrub are an exception to this rule.
Don't draw dense rows of bushes creating a single array as separate bushes.
In the picture, bushes that can be drawn as separate items are framed in green frame, while those that cannot are framed in red:

For other polygons of these types, you can assign detailed vegetation attributes to polygonal objects in general (see 3.9.4.2).
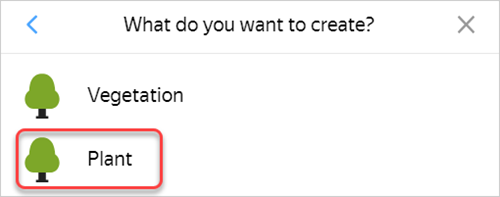
To create a Plant item:
-
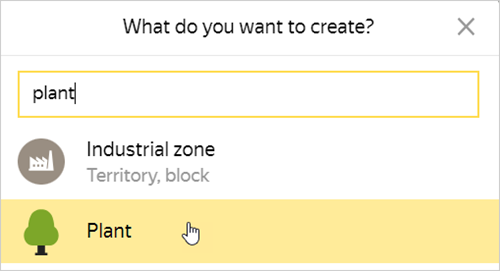
Click Create and choose a Plant item in the Vegetation category or the search bar:
-
Set the placemark in the center of a vegetation item:
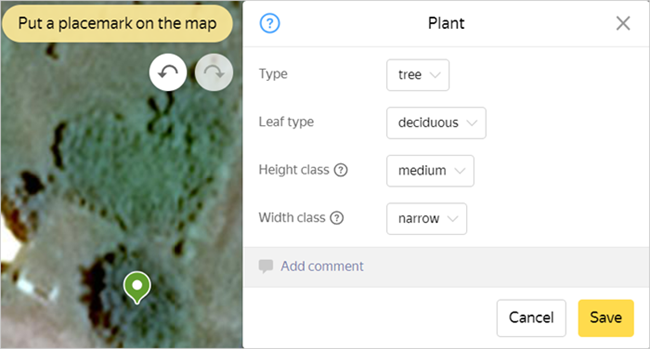
Note
Draw trees by following the base of their trunks rather than the geometric center of their crowns (if the data is complete and good enough to accurately decrypt it).
-
Set the values for the object's attribute:
-
Type: Tree/shrub.
Determine the plant type based on available open sources and your personal knowledge of botanical definitions.
-
Leaf type — coniferous/deciduous/palm.
Determine the plant type based on available open sources and your personal knowledge of botanical definitions.
-
Height class: high/medium/low.
Determine the height based on available open sources and your personal knowledge. To define a plant's approximate height, you can compare it with buildings, other surrounding items, or a person. If you can't determine the exact height, err on the lower side:
- Tree:
- Huge tree — > 40 meters.
- Very tall — 20-39 meters.
- Tall — 10-19 meters.
- Medium — 5-9 meters.
- Short — < 4 meters.
- Shrub:
- High — >2 meters.
- Medium — 1-2 meters.
- Short — < 1 meter.
-
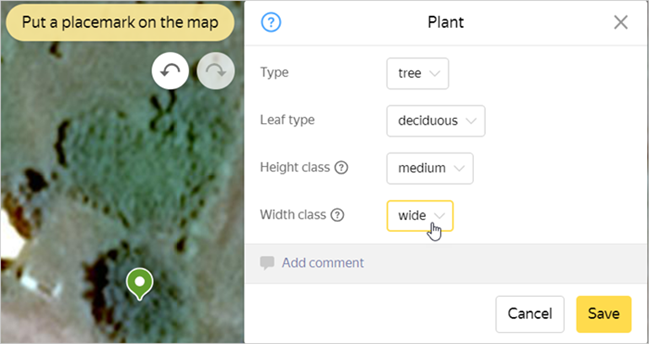
Width class: wide/narrow.
Use a ruler to measure the diameter of the plant's crown (same gradation for trees and shrubs). If you can't determine the exact width, set wide by default:
- Narrow — < 3 meters.
- Wide — >3 meters.
-
-
Click Save.

3.9.4.2. Adding attributes to polygonal items
If you can't distinguish free-standing trees and shrubs, you may assign detailed vegetation attributes to polygonal items.
You can either create a new vegetation item with the appropriate attributes or edit an existing polygonal object (see 3.9.1. Rules for drawing vegetation items).
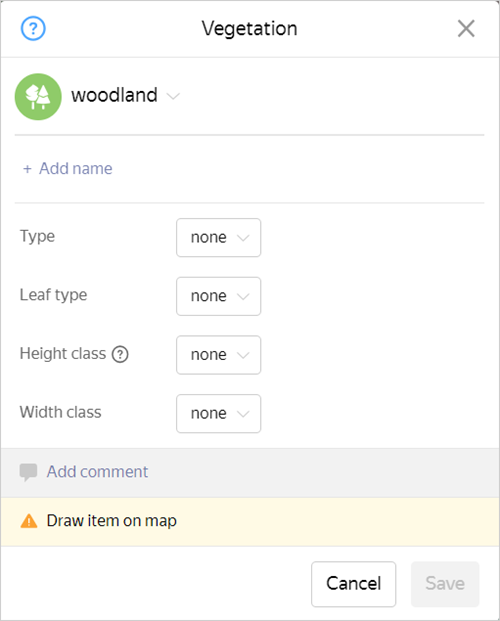
To attribute a polygonal vegetation item:
-
Choose or create an item:
-
Set the values for the object's attribute:
-
Type: Tree/shrub.
Determine the plant type based on available open sources and your personal knowledge of botanical definitions.
If an array contains both classes, set the prevailing value.
-
Leaf type — coniferous/deciduous/palm/mixed.
Determine the plant type based on available open sources and your personal knowledge of botanical definitions.
Set the
Mixed
value for arrays that contain mixed coniferous and deciduous instances. -
Height class: high/medium/low.
Determine the height based on available open sources and your personal knowledge. To define a plant's approximate height, you can compare it with buildings, other surrounding items, or a person. If you can't determine the exact height, err on the lower side:
- Tree:
- Huge tree — > 40 meters.
- Very tall — 20-39 meters.
- Tall — 10-19 meters.
- Medium — 5-9 meters.
- Short — < 4 meters.
- Shrub:
- High — >2 meters.
- Medium — 1-2 meters.
- Short — < 1 meter.
If an array contains trees with different heights, set the prevailing value.
-
Width class: wide/narrow.
Use a ruler to measure the diameter of the plant's crown (the same gradation for trees and shrubs). If you can't determine the exact width, set wide by default:
- Narrow — < 3 meters.
- Wide — >3 meters.
If an array contains both classes, set the prevailing value.
-
-
Click Save.
Draw polygons with highly detailed attribution according to the following rules:
-
-
You can only set these attributes for urban and forest vegetation items. Don't set attributes for the polygons of free-standing plants.
-
If you can visually distinguish multiple polygons with different predominant features (such as adjacent areas of coniferous and deciduous trees) in a single vegetation array, create multiple contours with different attributes:
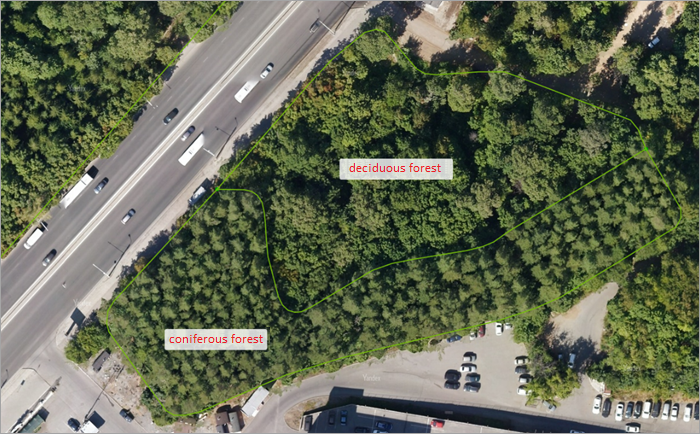

-